 Transposable elements ("jumping genes") are DNA sequences
that can move from one chromosome locus to another.
Transposable elements ("jumping genes") are DNA sequences
that can move from one chromosome locus to another.
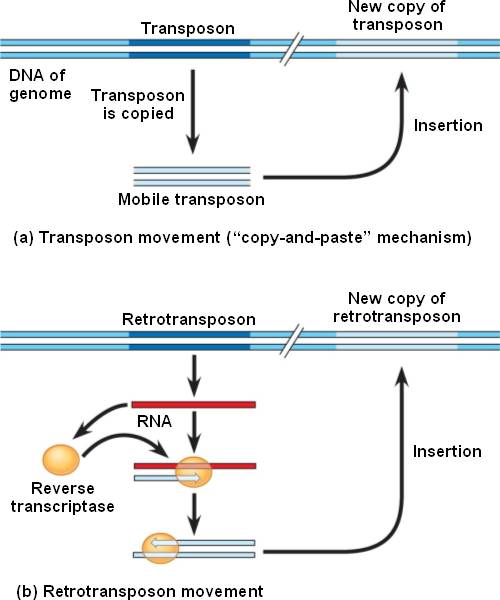
- Transposons move by means of a DNA intermediate.
First the DNA is copied to a mobile fragment, which is inserted elsewhere.
- Retrotransposons move by means of an RNA intermediate.
The segment is first trancribed to RNA, then reverse transcriptase makes the DNA mobile fragment,
followed by insertion.
Often this results in gene duplication.
 Transposable elements ("jumping genes") are DNA sequences
that can move from one chromosome locus to another.
Transposable elements ("jumping genes") are DNA sequences
that can move from one chromosome locus to another.